Hearing protection – Preventing irreversible injuries
Noise at the work place is frequently underestimated
Hearing protection refers to all kinds of protective devices and equipment which protects hearing from excessively loud noises and prevents acoustic trauma. The effects of loud noise and continuous noise can make us ill and adversely affect performance.
Noise, especially at the workplace, is often underestimated and the dangers of noise go unrecognised.
In Europe, noise-induced loss of hearing is an increasingly serious problem and is the most frequently reported occupational illness. When hearing is lost due to noise, sound waves have damaged the hair cells in the inner ear. Once they have died away, they cannot grow back.
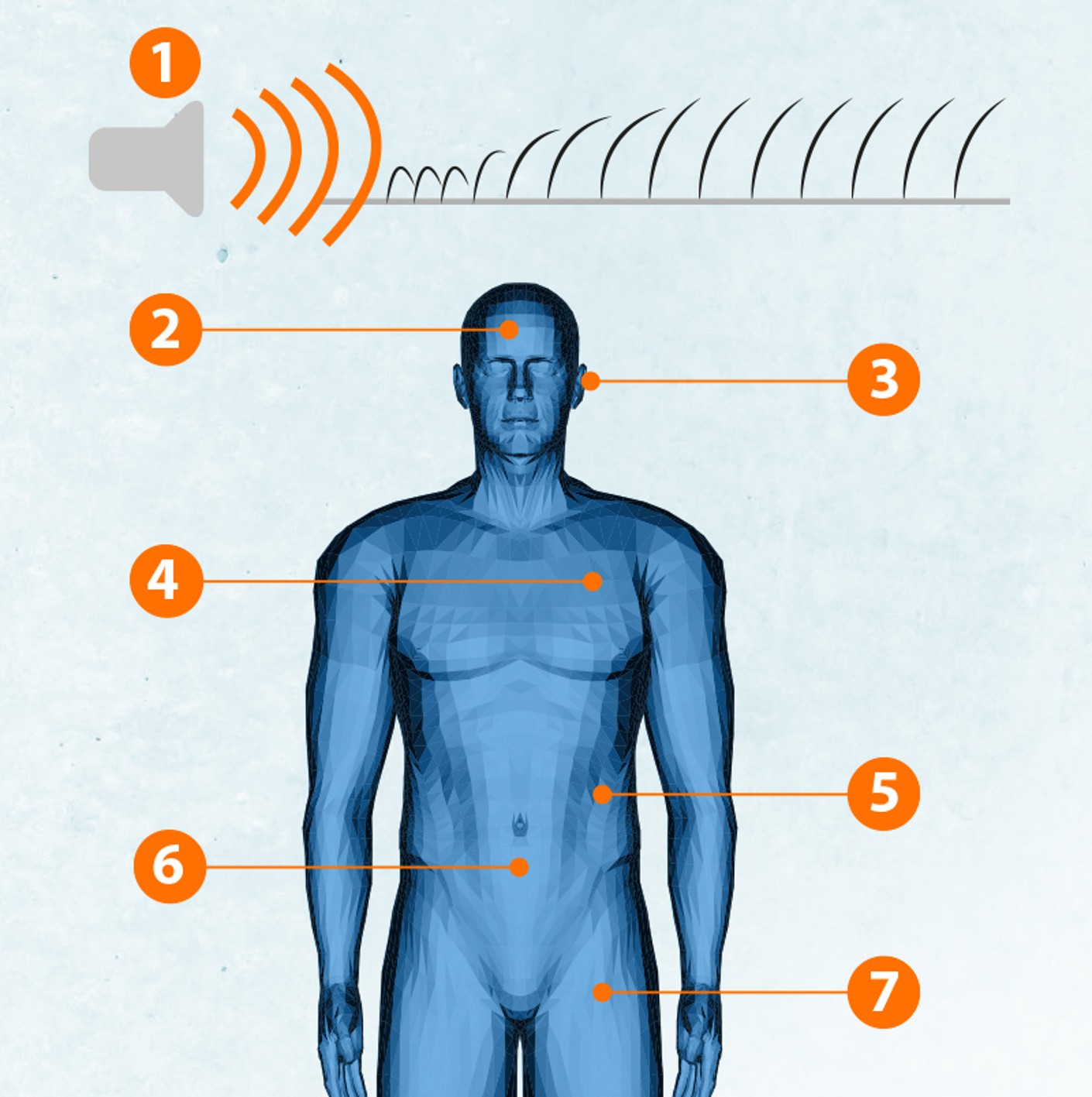
The illness is so vicious because is creeps up on you insidiously and is incurable. At first, affected people do not hear the higher tones. Only later is perception of the middle and lower tones impaired.
This is particularly tragic because with the correct hearing protection every single case of noise-induced loss of hearing is 100% avoidable.
Noise has a damaging effect not only on our hearing, it can generate damaging effects on the entire body. Noise stress can cause headaches, metabolic problems, digestive complaints and many other complaints.
- Headaches
- Tinnitus, hearing loss
- Increased risk of heart attack and high blood pressure
- Increase adrenaline flows with resulting metabolism issues
- Digestion problems
- Reduced blood flow
At what point must hearing protection be worn?
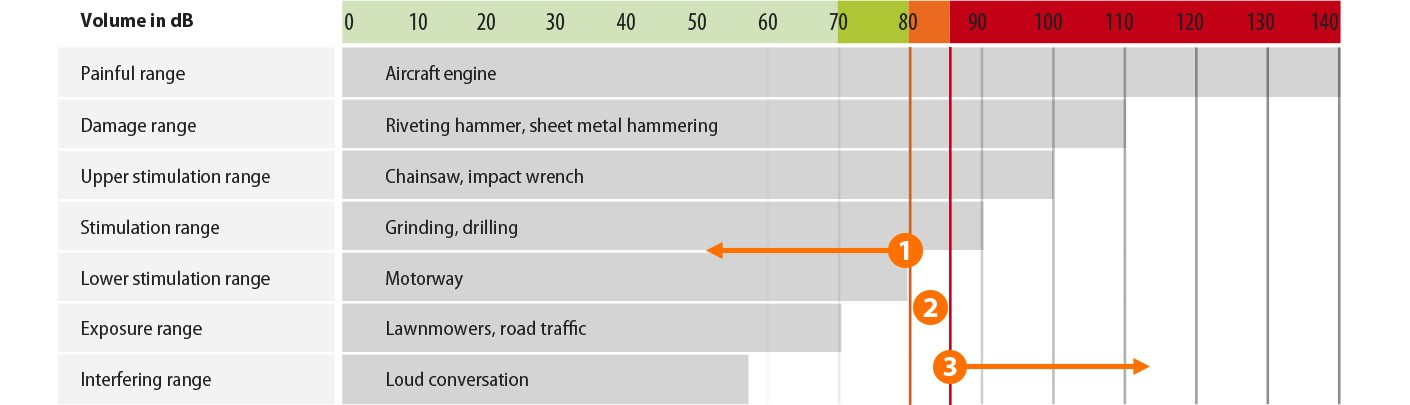
A noise is the result of vibrations propagated in the air as pressure waves. The more powerful the pressure waves the louder the noise. These can be measured and are stated in the unit decibel (dB). The stress of a noise level for the ear is stated in the unit dB(A).
The protection of employees in a noisy working environment is regulated by the EC Noise Exposure Directive 2003/10/EC. This clearly specifies that at noise levels of 80 dB and above, hearing protection must be provided by the employer and that at noise levels 85 dB and above suitable hearing protection must be worn by the employee:
- No obligation to wear: ⌀ Noise level< 80 dB, noise pulses < 135 dB
- Supply but no obligation to wear: ⌀ Noise level 80 dB to 85 dB or noise pulses 135 dB to 137 dB
- Supply and obligation to wear: ⌀ Noise level > 85 dB, noise pulses > 137 dB
The technical safety requirements specified in EN 352-1 to EN 352-8 must be satisfied.
Select the right hearing protection
The following points must be taken into account when choosing hearing protection:
- Determine the noise level at the workplace.
- Respect personal preferences, since these can have a decisive effect on wearer acceptance.
- Note the SNR value for hearing protection products: This specifies how much the product reduces the prevailing noise levels.
- If the frequency is known exactly, we recommend that the hearing protection is selected according to the H value (high frequency), M value (medium frequency) or L value (low frequency). Most industrial production processes generate predominantly medium frequency noise stress.
- Do not choose noise insulation that is too high: below 70 dB residual noise level means too much protection, which leads to comprehension issues and feelings of isolation.
- Residual noise level should be between 70 and 80 dB.


Variance: Depending on the type of hearing protection used, a correction value to allow for variance must be included: 5 dB for shell-type ear protectors; 5 dB for re-usable earplugs; 9 dB for disposable earplugs; and 5 dB for banded earplugs. The residual noise level can be determined as shown above.
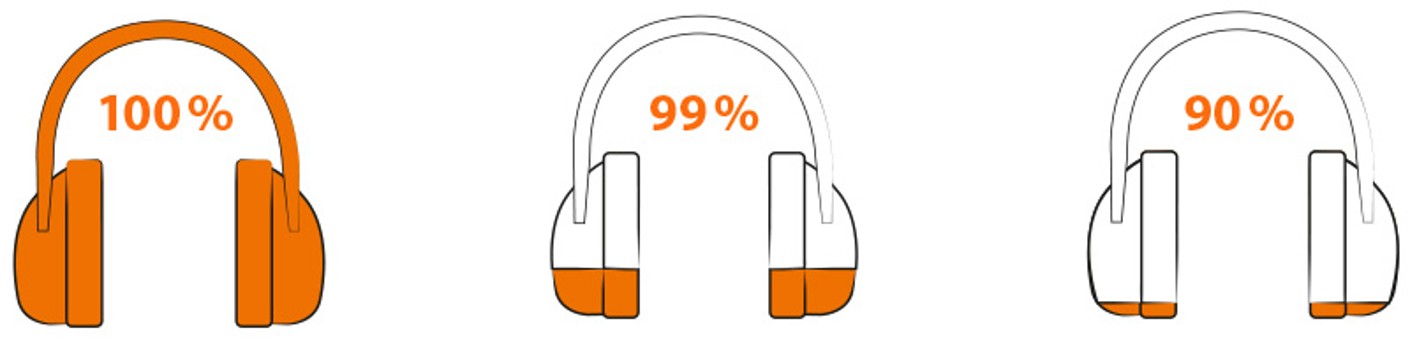
Important: Make sure that the hearing protection is worn 100% of the time in noisy working environments. Even short periods during which hearing protection is not worn lead to complete loss of the protective effect.
Do you have any questions? Our experts are keen to help you at any time:
Type of hearing protection

Selection criteria for the right hearing protection
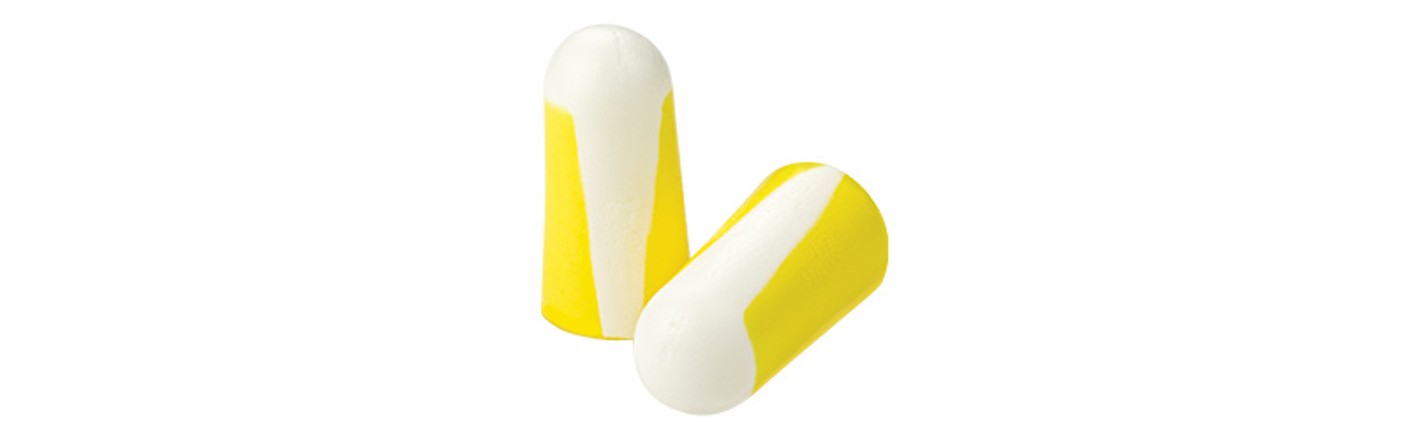
Disposable earplugs
Earplugs are basically inserted into the auditory canal and are especially well-suited to moist and warm environments. They also have good attenuation levels due to filtration of the noise levels, even at low frequencies.

Advantages:
- No perceptible weight, or only very small weight.
- Can be combined with other protective equipment.
- No heat build-up.
- High availability from dispenser systems.
Disadvantages:
- Incorrect insertion reduces the attenuation performance.
- Pressure sensation when worn for long periods.
- Less suitable for fluctuating noise conditions.
In order to obtain the SNR values and hence optimum protection, correct insertion of the earplug is of critical importance.
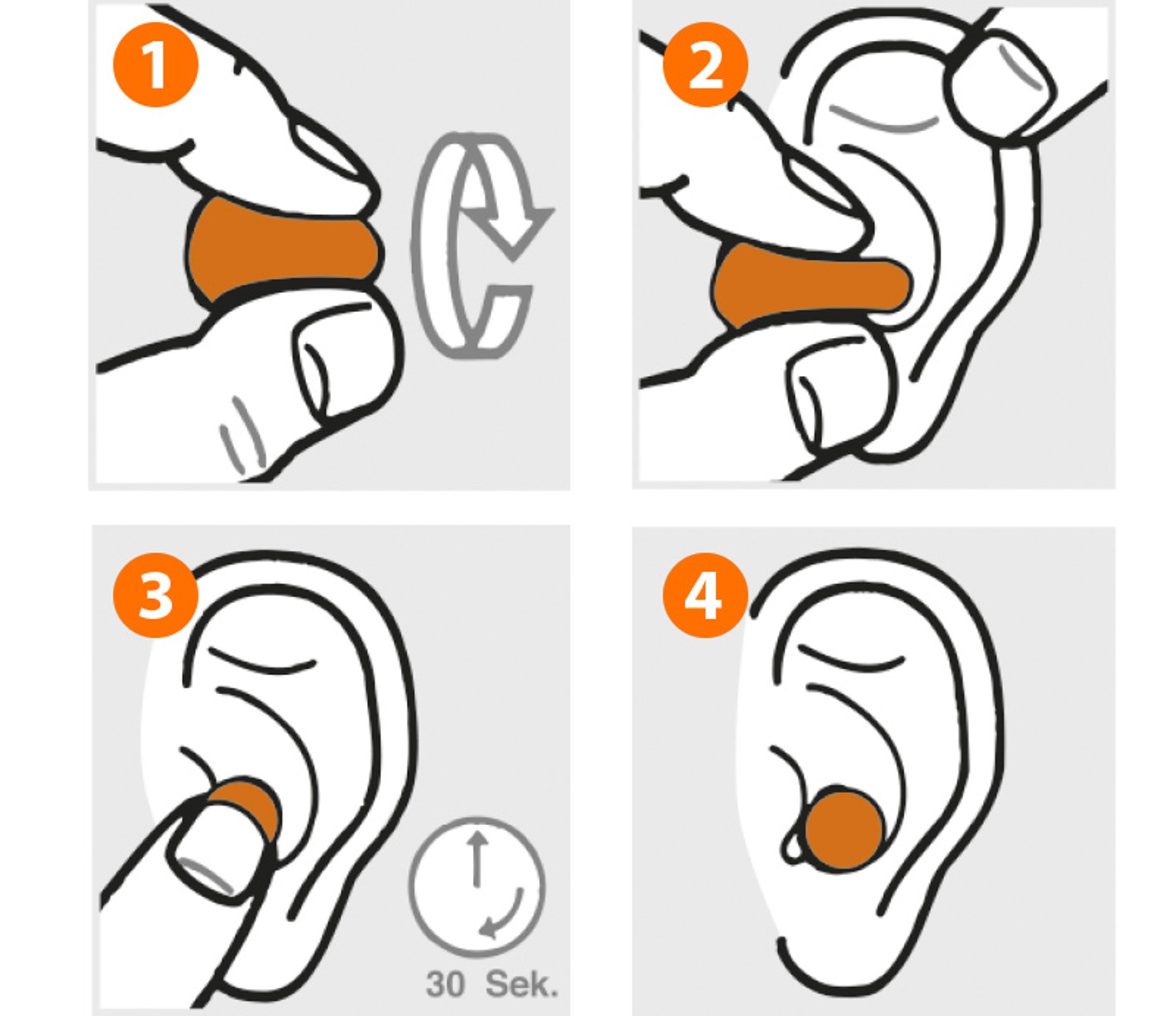
This is how to insert disposable earplugs correctly:
1. Roll the plug up as small as possible, taking care not to fold it. Make sure your hands are clean.
2. Reach over your head with your free hand and pull the ear upwards and backwards. Insert the plug deeply into the auditory canal.
3.& 4. Hold the plug firmly for approx. 30–40 seconds until it has fully expanded within the auditory canal. The earplugs are seated correctly in the ear if nothing is visible when viewed from the front.
This is the correct way to remove and dispose of earplugs:
When removing the earplug, pull it slowly out of the auditory canal with a slight twisting action.
After use, disposable earplugs should be disposed of in the correct manner.
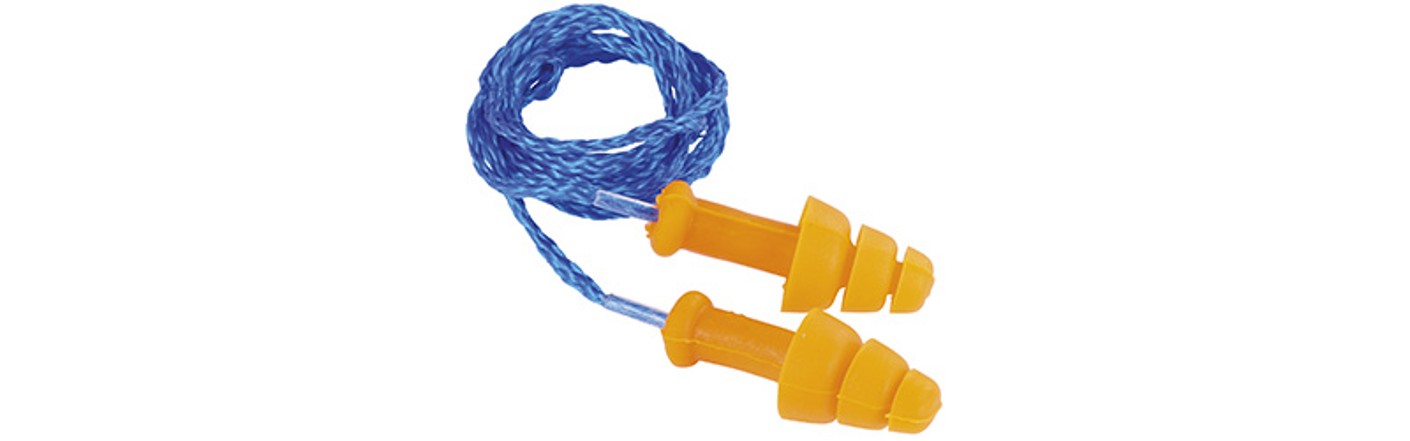

Re-usable earplugs
Earplugs are basically inserted into the auditory canal and, due to the washable surface, they can be used again without losing their original shape. When you leave a noisy area, the earplugs can be put away in a handy storage box.

Advantages:
- No perceptible weight, or only very small weight.
- Can be combined with other protective equipment.
- The cord means you won’t lose them.
- Storage box for safe retention.
Disadvantages:
- Incorrect insertion reduces the attenuation performance.
- Pressure sensation when worn for long periods.
- Less suitable for fluctuating noise conditions.
In order to obtain the SNR values and hence optimum protection, correct insertion of the earplug is of critical importance.
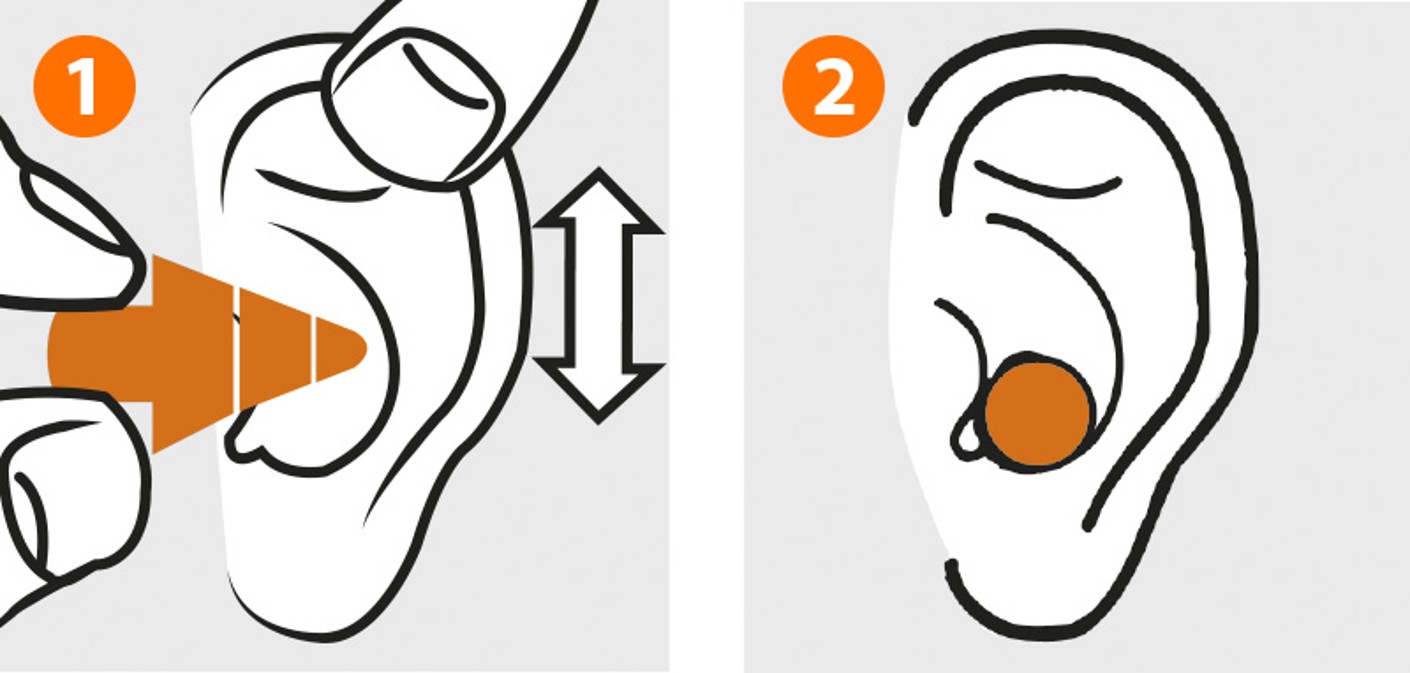
This is how to wear earplugs correctly:
- Use one hand to grip the earplug by the stalk. With the other hand, pull the ear upwards and backwards whilst inserting the earplug into the auditory canal. Pulling the plug up and down during insertion increases the protective effect.
- Even when correctly seated, the plug remains visible from the outside.
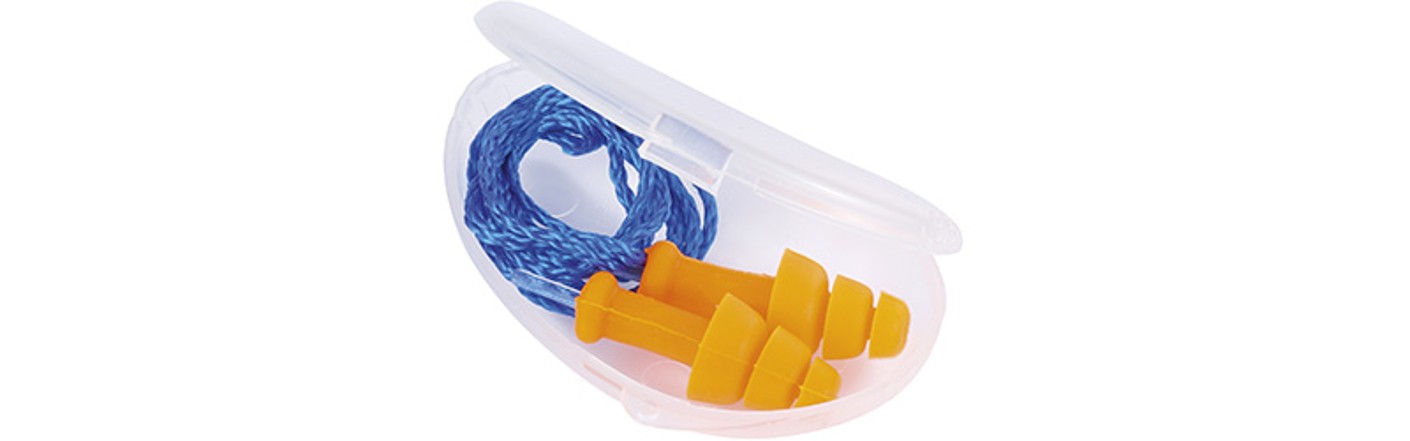

Storage boxes:
A small storage box, with a belt clip or kidney shape depending on the manufacturer, permits handy storage of earplugs when not in use. The cord means that the earplugs can be carried round the neck during breaks in work. Make sure your clothing is clean.
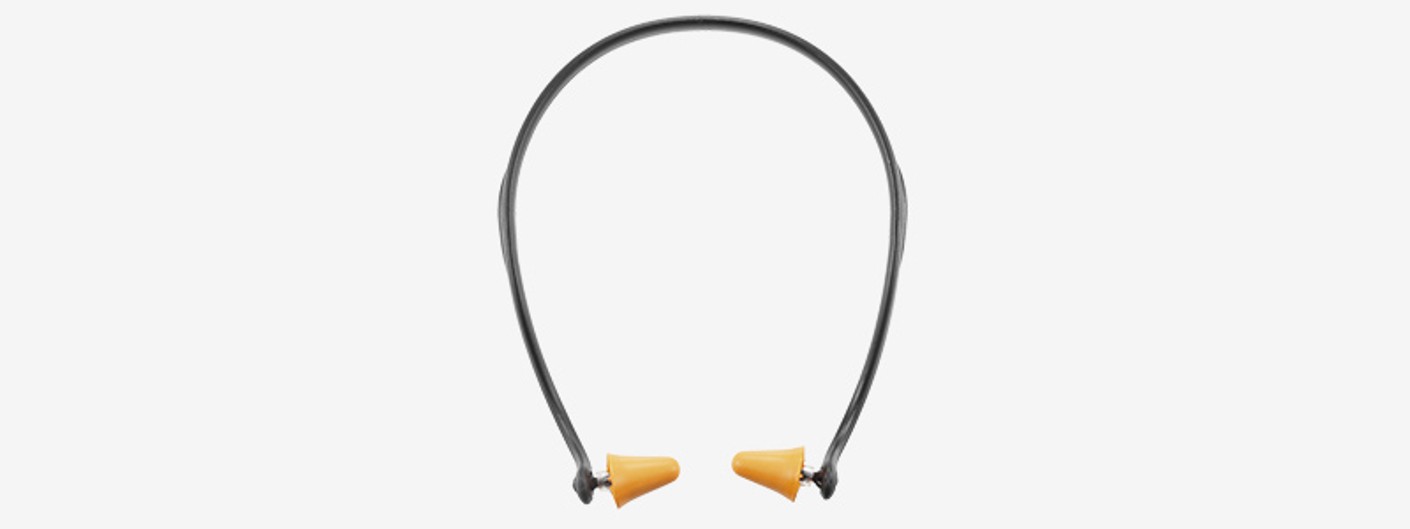

Banded earplugs
Banded earplugs are easy to use, comfortable to wear and can be put on and taken off quickly. The earplug does not sit in the auditory canal, instead it closes off the outer opening of the canal, which makes it pleasant to wear. It is suitable for working environments with high temperatures, since no heat build-up occurs. Earplugs can be replaced and the band can be re-used.

Advantages:
- Quick and easy positioning.
- Pleasant to wear.
- Low weight.
Disadvantages:
- Low attenuation performance.
- Noise transmission through rubbing protective work wear.
- Incorrect insertion reduces the attenuation performance.
In order to obtain the SNR values and hence optimum protection, correct insertion of the earplug is of critical importance.
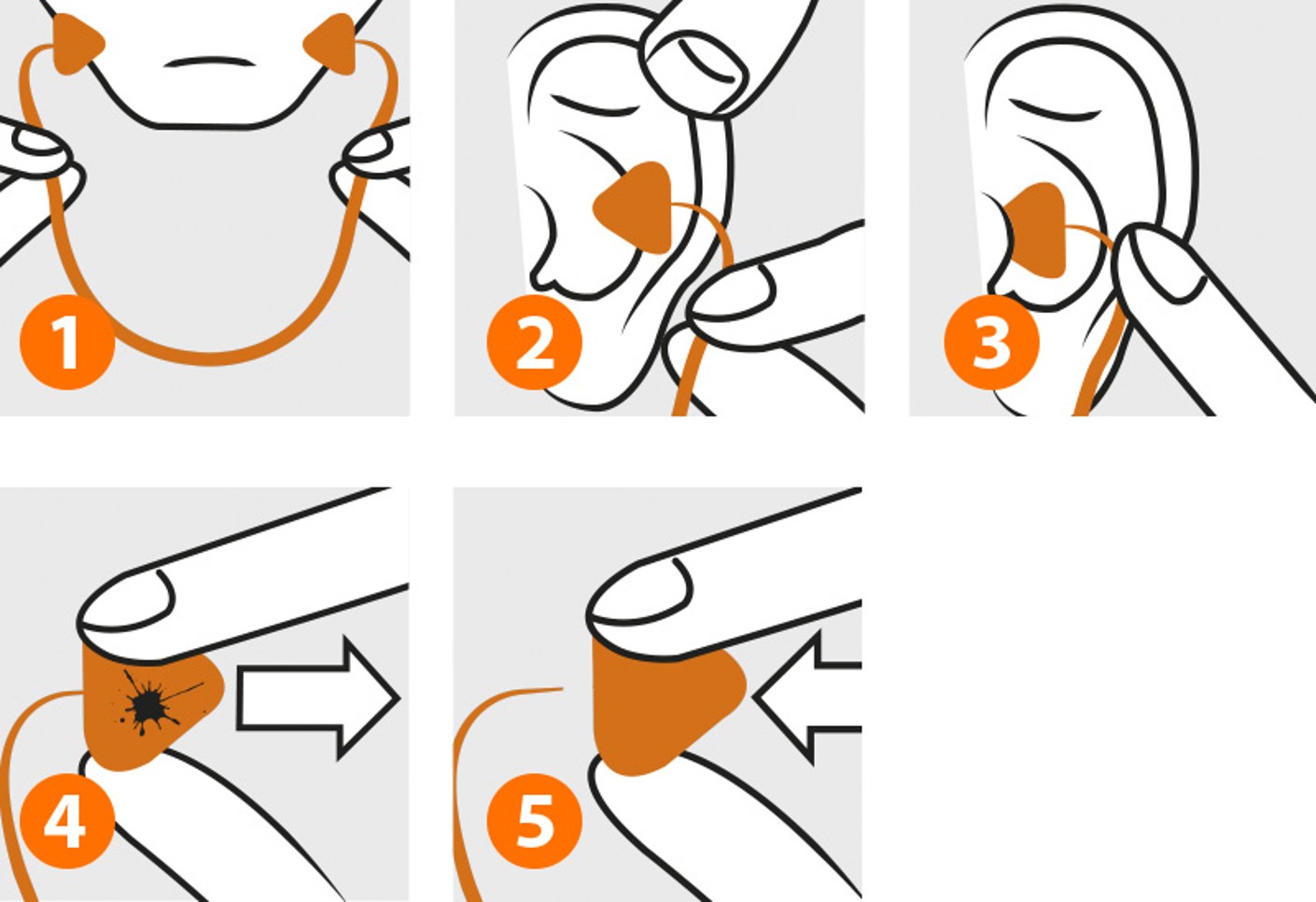
This is how to wear banded earplugs correctly:
- Grip the band under the chin with both hands.
- Pulling the ear upwards and downwards whilst inserting the earplug increases the attenuation rating.
- To check the seating, in a noisy environment press both earplugs slightly inwards. This should not make any great difference to the noise.
This is how to exchange the earplugs on banded ear defenders:
4. Pull the dirty earplug off the band.
5. Insert the new earplugs on to the band with a slight twist.
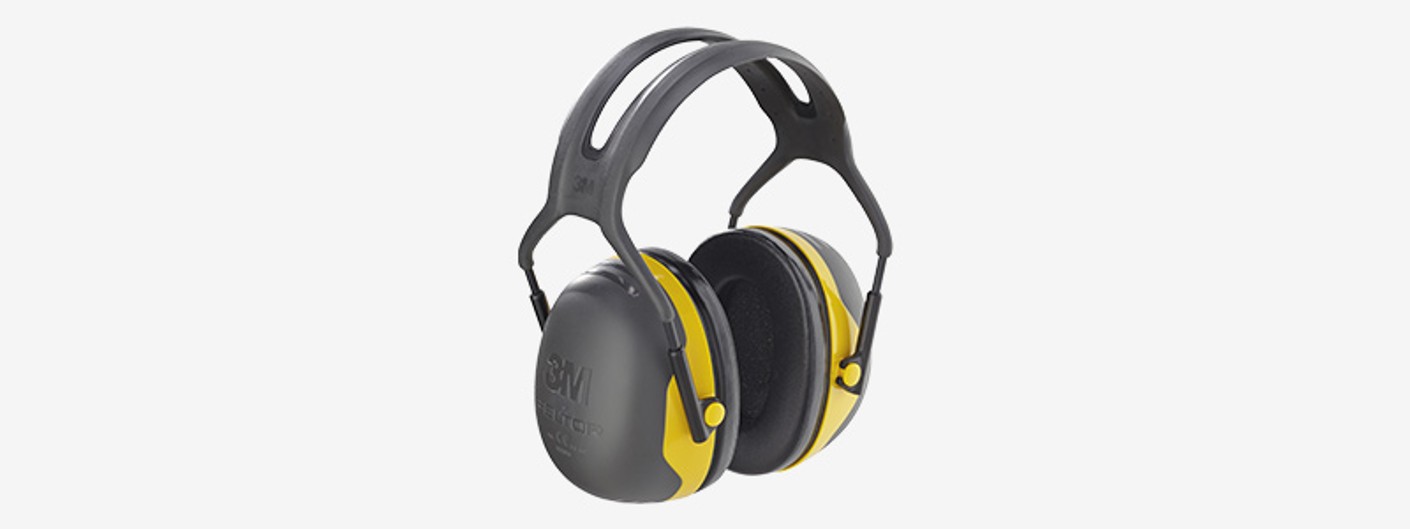

Shell-type ear defenders
Shell-type ear defenders are particularly suitable for use in dirty environments and in environments where the noise level is continually changing. The capsule envelopes the entire ear, so the headband provides stable and comfortable seating. Nothing is inserted into the auditory canal. They are particularly suitable for persons whose auditory canals are very narrow and sensitive to pressure. Head straps, neck straps and chin straps are available with suitable mountings for use on safety helmets.

Advantages:
- High attenuation rates can be achieved.
- Easy to operate.
- No sensation of pressure in the ear.
- Easy to check if they are being worn.
Disadvantages:
- Sweating under the shell.
- Higher weight.
- Cannot always be combined with other protective equipment.
In order to obtain the SNR values and hence optimum protection, correct insertion of the earplug is of critical importance.
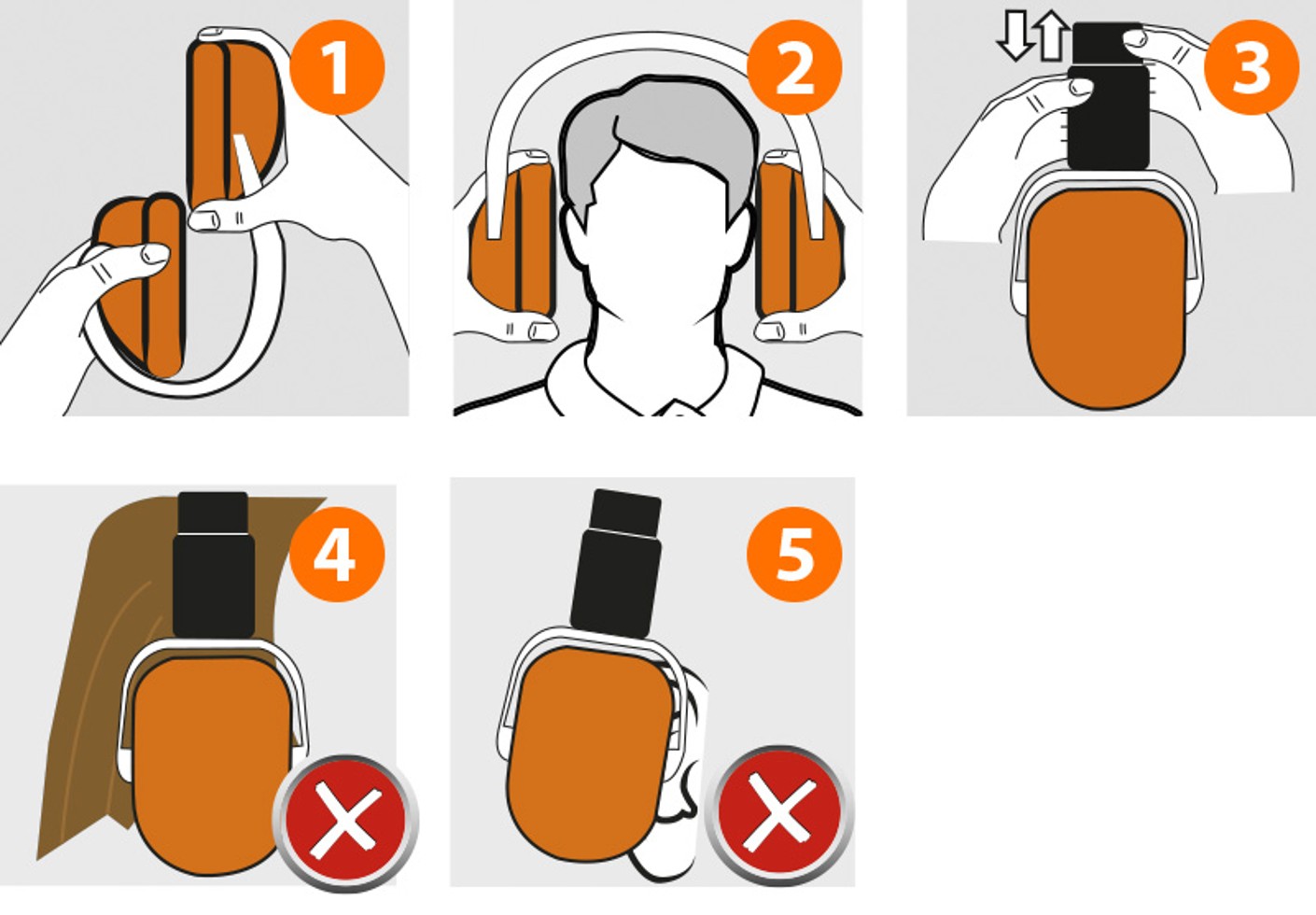
This is how to wear shell-type ear defenders correctly:
1. Fold-away shell-type ear defenders from inwards to outwards.
2. Place the shells over your ears.
3. Adjust the position of the band upwards and downwards.
The following should be taken into account during use:
4. In order to avoid leakage, hair and the arms of glasses should not lie between the ear defender and the ear.
5. The ears should no longer be visible.
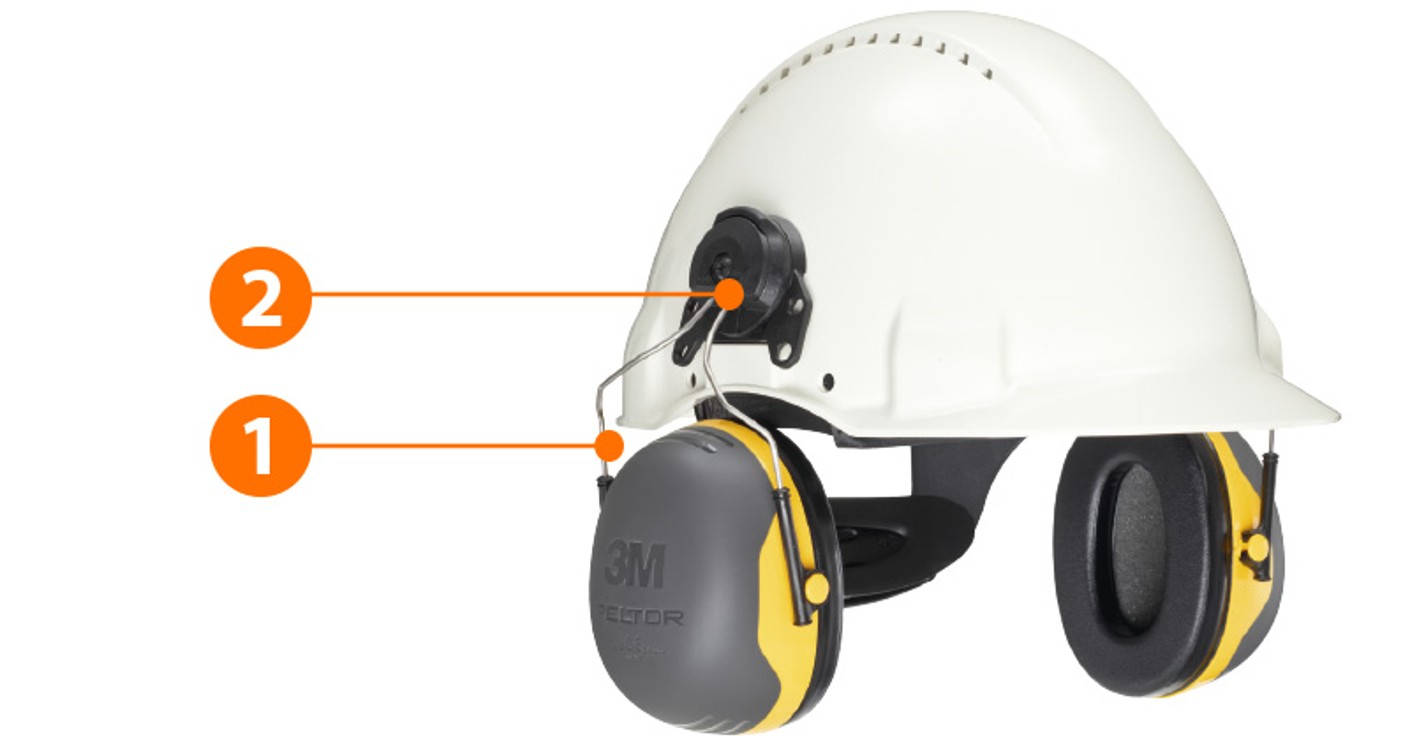

In combination with a safety helmet:
- The shell-type ear defenders can easily be put on or taken off by clicking on and off.
- When the ear defenders are not in use they can easily be swung away upwards.
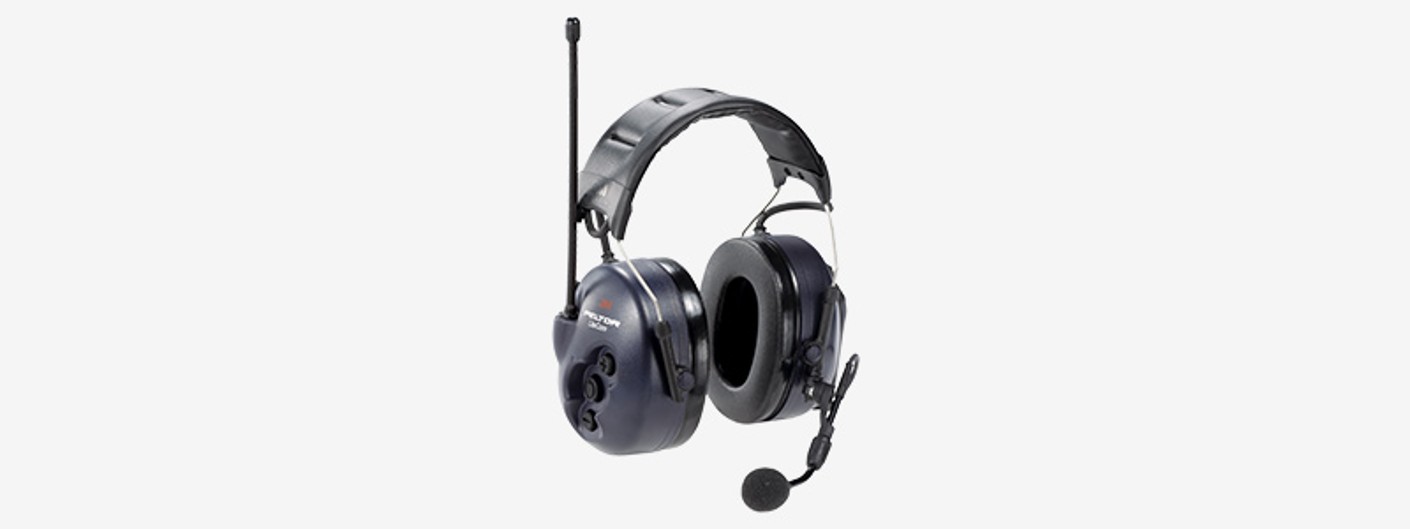

Electronic hearing protection
Hearing protection with special functions enables communication and simultaneous protection in the event of high noise levels. The noise-level-dependent attenuation technology means that warnings and instructions can audibly be received. Harmful noise is damped to a level less than 82 dB in order to protect hearing. Warning signals, discussions and process sounds are easily perceptible and communication over great distances in conjunction with mobile phones and radio devices is disruption-free. Additional functions, such as volume regulation of level-dependent functions, balance control, equalizer and volume control for external input signals, are available.

Advantages:
- For demanding working environments.
- Communication by radio or mobile phone.
- Built-in conversational electronics fur use when work is monotonous.
- Environmental noises are heard but noise pulses are automatically blocked off.
- Increases in productivity and motivation of employees
Disadvantages:
- Unsuitable for occasional wearing.
- Higher weight.
- Heat build-up under the shell.
In order to obtain the SNR values and hence optimum protection, correct insertion of the earplug is of critical importance.
As the Safety Officer in your company, are you responsible for the annual instructions? This video deals with all the relevant points that are required for the annual hearing protection instructions according to the guidelines of the DGVU (German Statutory Accident Insurance).
Diverse product range and personal consulting

At the Hoffmann Group, you will find a wide range of hearing protection products from selected and high-quality manufacturers for various fields of application: from the production hall to the construction site, right through to working in the forest or private use. We are able to supply high-quality earplugs and dispensers , banded earplugs , shell-type ear protectors , electronic hearing protection and matching accessories .
Benefit from our know-how in the field of PPE: We will accompany you on all relevant topics from risk analysis, product selection and wear tests to training for your employees. Our highly qualified team of specialists will advise you personally on the subject of hearing protection at any time: Contact us in person, by phone or e-mail.

Directives and standards for hearing protection
On 21 April 2018 the PPE regulation 2016/425 superseded the previous directive 86/686/EEC. This resulted in substantial changes to the classification of products in the field of personal protective equipment. As a result, the EU recognised that harmful noise causes irreversible harm to health and raised the classification of hearing protection products to risk category III. Special provisions are applicable to products in risk category III. Accordingly, in many EU member states, practical instruction by the company of the employees for category III protective equipment is a mandatory requirement. From 21 April 2019, manufacturers are only allowed to introduce to market hearing protection products in compliance with the new PPE regulation.
The following European standards apply to hearing protection:
EN 352-1: Shell-type ear defenders
EN 352-2: Earplugs
EN 352-3: Helmet ear defenders
EN 352-4: Level-dependent shell-type ear defenders
EN 352-5: Shell-type ear defenders with active noise compensation
EN 352-6: Shell-type ear defenders with communication equipment
EN 352-7: Level-dependent attenuating earplugs
EN 352-8: Audio shell-type ear defenders for conversational applications (e.g. radio)
EN 458: Recommendations for the selection, use, care and maintenance of hearing protection
Frequently asked questions on hearing protection
From which volume must hearing protection be worn?
Hearing protection must be worn from a daily noise exposure level of 85 dB or a peak sound pressure level of 137 dB. According to the German Technical Regulations Governing Noise and Vibrations (TRLV), people with existing inner ear damage should consistently wear hearing protection from a daily noise exposure level of 80 dB and upwards.
Up to which noise level can you wear earplugs?
This depends on the type of SNR value (attenuating) of the earplug. Taking the correction value into account, an earplug with a high attenuation level can be used at higher noise levels than an earplug with a low attenuation level.
Is the hearing protection used adequate for the activity?
Selection programmes, which are available on a CD or on the Internet, are available for selecting the appropriate hearing protection.
What does hearing protection do in terms of noise reduction?
The level reduction can be 15–32 dB(A) for earplugs and 19–28 dB(A) for shell-type ear defenders.
How were the limits determined?
A panel of experts on “personal protective equipment” conducted an interlaboratory test with four analysis labs for certain constituent materials. In this process, different verification methods were also strategically employed. Suitable methods of analysis and quality criteria were defined based on the experiences from the interlaboratory tests. The levels of the individual limits were defined with the involvement of experts from the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the German Social Accident Insurance (BGIA) and taking account of the state of the art.

Do you have any questions? Would you like to receive advice on PPE?
The Hoffmann Group provides you with everything from a single source:
- We provide individual advice, tailored to your needs
- Risk analysis, help with product selection, wearing tests, training sessions and special service offers (glove plans, skin protection plans)
Personal protective equipment also includes: eye protection, breating protection, head protection, foot protection, hand protection, protective work wear, work clothing, fall protection and skin protection.
This takes you to overview.











 Contact us now
Contact us now